5 Lose Weight Surgery Options
-
 Written by
Michael J. Ormsbee
Written by
Michael J. Ormsbee
- LAST UPDATED November 9, 2023
Addressing obesity, a major and escalating global health problem, is critical as it affects both physical and mental health. Obesity predisposes individuals to a host of harmful health complications such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. Therefore, maintaining a balanced and healthy weight is key to enhancing overall health. For those with severe obesity who have been unsuccessful with conventional weight loss approaches like diet and exercise, there are lose weight surgery options available. Bariatric surgery, one of such options, provides an effective long-term solution.
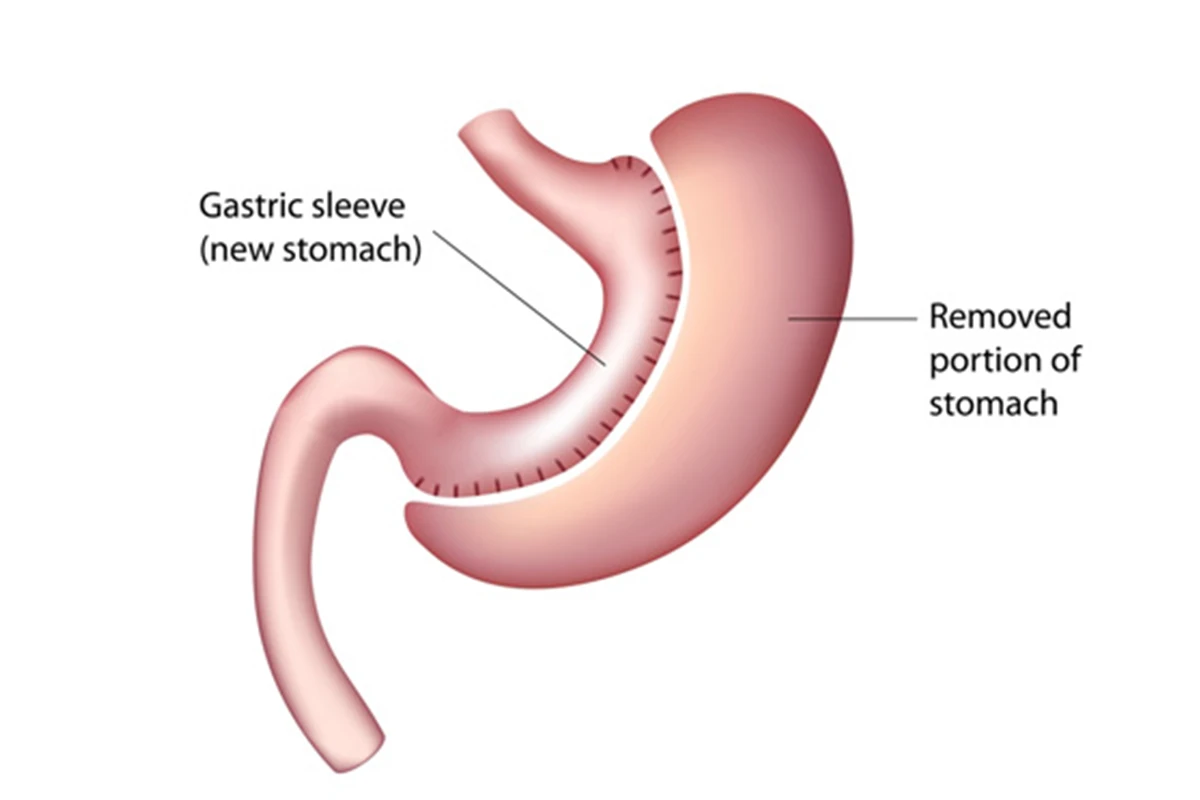
Gastric Sleeve (Sleeve Gastrectomy)
Within the spectrum of lose weight surgery options, gastric sleeve surgery, or sleeve gastrectomy, is a widely chosen procedure. This operation entails the removal of about 80% of the stomach, leaving behind a small, banana-shaped sleeve. By significantly reducing the stomach’s ability to hold food, this surgery assists in promoting a sensation of fullness more rapidly, thereby lowering overall calorie consumption.
Advantages of gastric sleeve surgery include a lower risk of complications compared to other bariatric surgery options and the potential for significant weight loss (50-70% of excess weight within two years). This surgery can also improve obesity-related health conditions like type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, and hypertension.
Potential complications and risks include leakage from the stomach, blood clots, infections, and nutritional deficiencies resulting from a smaller stomach and reduced food intake.
Gastric Bypass (Roux-en-Y)
When exploring various lose weight surgery options, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, commonly known as gastric bypass surgery, is another commonly considered choice. The procedure is characterized by creating a small pouch from the stomach and then rerouting the small intestine to this pouch. Consequently, it effectively limits an individual’s food intake and reduces nutrient absorption, further contributing to weight loss.
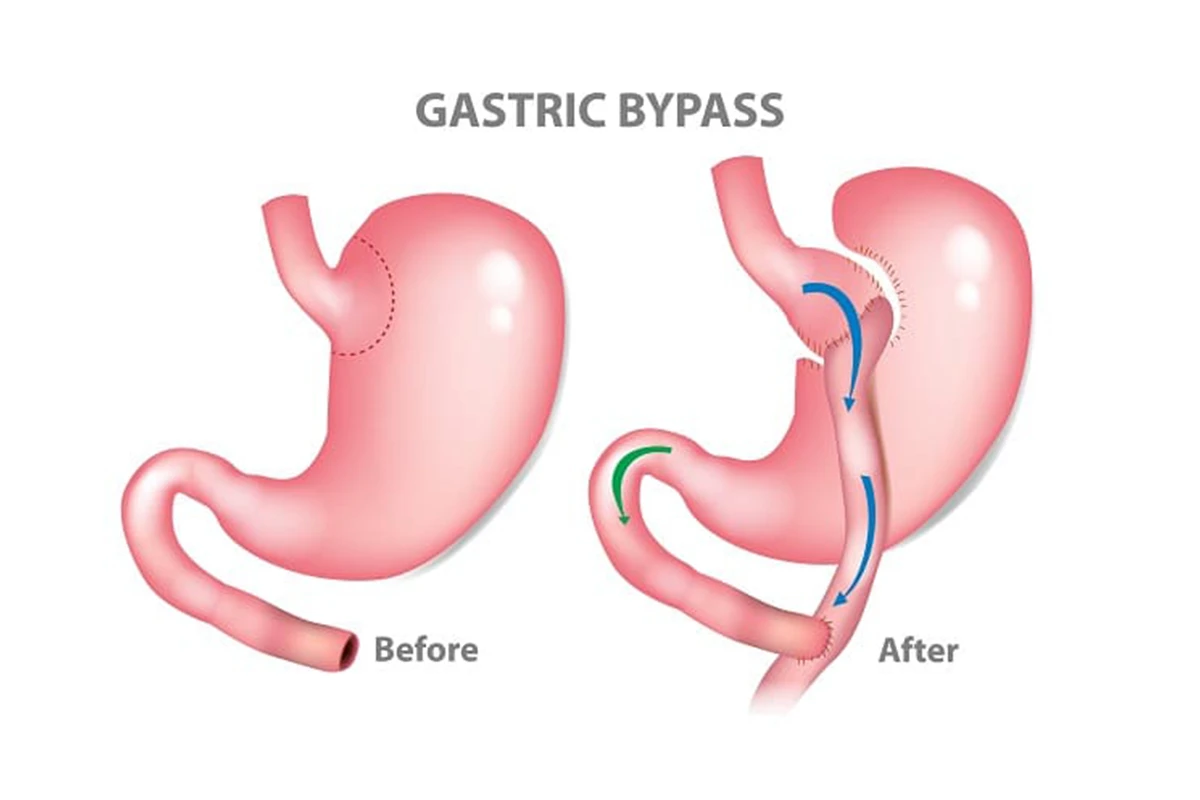
In considering different lose weight surgery options, gastric bypass surgery stands out with its range of benefits. These benefits include a significant and swift reduction in weight, with patients typically losing 60-80% of their excess weight in the first one to two years. Moreover, this surgical approach contributes to improved health outcomes for obesity-related conditions like type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, and high blood pressure.
Potential complications and risks include staple line leakage, infection, blood clots, and nutritional deficiencies due to altered digestion and absorption of nutrients.

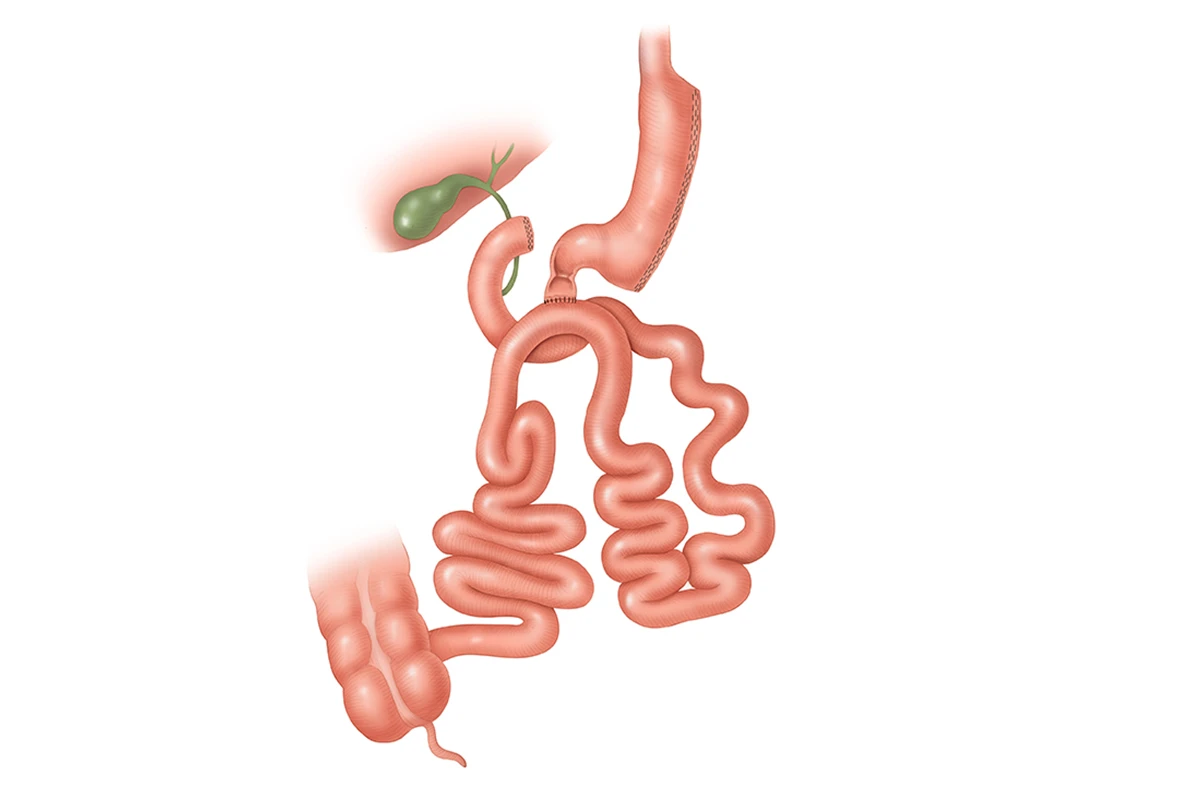
Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD-DS)
Among the multitude of lose weight surgery options, the Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD-DS) is more complex yet effective. This unique approach combines both restriction and malabsorption techniques for weight loss. The procedure involves two major steps: firstly, resizing the stomach into a smaller, tubular form through the removal of a significant portion, and secondly, rerouting a sizeable portion of the small intestine to bypass the absorption of calories and nutrients.
When it comes to weighing the benefits of various lose weight surgery options, the Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD-DS) is notable. This procedure frequently leads to massive weight loss, often resulting in patients losing 70-80% of their excess weight. Moreover, it contributes to the reduction of comorbidities such as heart disease and diabetes. Additionally, patients who choose BPD-DS have a lower risk of weight regain compared to those who undergo other types of bariatric surgeries.
Potential complications and risks include nutritional deficiencies, malabsorption, infections, blood clots, and surgical complications such as leakage from the staple line.
Stomach Intestinal Pylorus Sparing Surgery (SIPS or Loop Duodenal Switch)
As we consider various lose weight surgery options, Stomach Intestinal Pylorus Sparing Surgery (SIPS), often referred to as loop duodenal switch, emerges as a modified version of the traditional duodenal switch surgery. The procedure entails the removal of a smaller section of the stomach and bypassing a loop of the small intestine instead of rerouting it. Lower invasiveness and reduced risk of complications make SIPS a noteworthy alternative to the more complex BPD-DS surgery.
Advantages of SIPS include substantial weight loss (50-70% of excess weight), improvement in obesity-related health problems, and a reduced risk of complications compared to other weight loss surgeries.
Potential complications and risks include malnutrition, dehydration, blood clots, and surgical complications such as leakage or infection.
Endoscopic Weight Loss Procedures
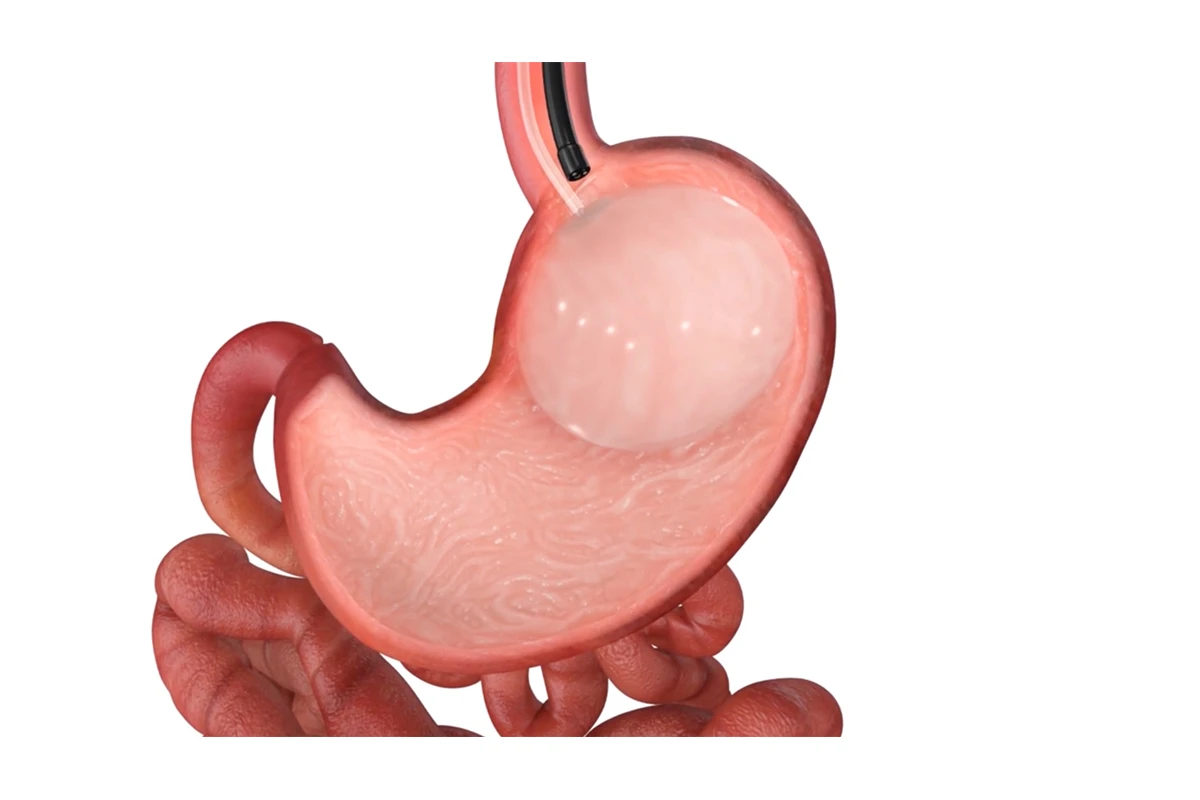
Intragastric Balloon
In the universe of lose weight surgery options, the intragastric balloon stands out as a non-surgical procedure. It involves the placement of a saline-filled silicone balloon in the stomach. This approach reduces the stomach’s capacity, enabling patients to feel fuller with less food. As a result, the patient’s overall calorie intake reduces, leading to weight loss. This treatment is a temporary solution in managing weight.
Advantages of the intragastric balloon include its non-invasive nature and the potential for moderate weight loss (20-40% of excess weight) for individuals who do not qualify for or are hesitant to undergo surgery.
Potential complications and risks include balloon deflation, migration, or rupture, nausea, vomiting, and gastric ulcers.
Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG)
When discussing lose weight surgery options, endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) is often at the forefront. It is a minimally invasive weight loss procedure that is executed using an endoscope. With ESG, the size of the stomach is shrunk by suturing the walls of the stomach to create a reduced, sleeve-like shape. Similar to other weight loss surgeries, ESG works by making patients feel full more quickly, hence scaling down the overall calorie intake.
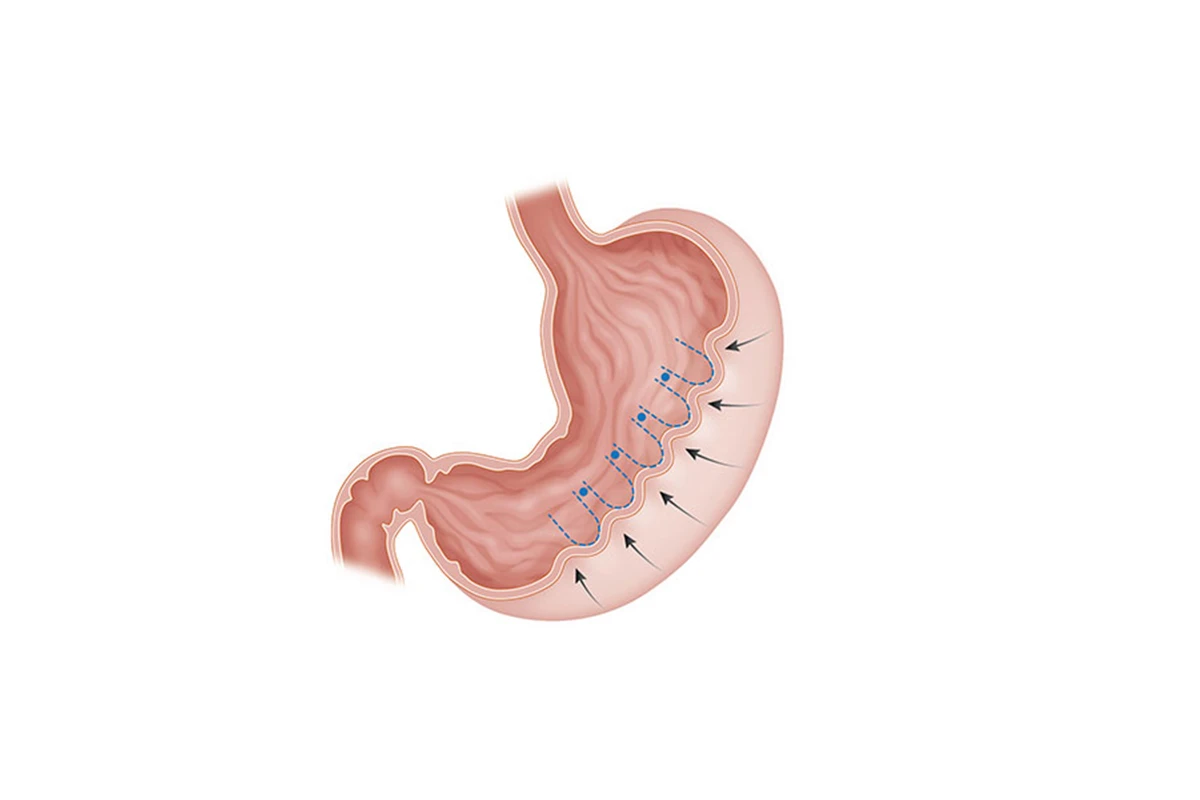
Advantages of ESG include its minimally invasive nature, the potential for moderate weight loss (20-40% of excess weight), and a lower rate of complications compared to other weight loss surgeries.
Potential complications and risks include bleeding, infection, leakage, and perforation of the stomach wall.
Lose Weight Surgery Options: Qualifications for Bariatric Surgery
In the realm of lose weight surgery options, candidates typically have a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or higher. Alternatively, they may have a BMI between 35 and 40 accompanied by at least one obesity-related health condition such as diabetes, hypertension, or sleep apnea. Beyond BMI, it’s important to note that medical and psychological evaluations are a necessary part of the process to determine a patient’s readiness and suitability for surgery.
Preparations for Bariatric Surgery Among Lose Weight Surgery Options
Bariatric surgery preparation is a multifaceted process that involves several crucial steps. Each aims to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the surgery, and the long-term success of your weight loss journey. This preparation process typically includes:
Preoperative Medical Tests
These comprehensive tests help analyze your health status and identify potential risks that could affect your surgery. The assessments may include:
- Blood tests: These tests may include liver function, kidney function, and a complete blood count. Doctors may also screen for nutritional deficiencies, hormonal disorders, or conditions like diabetes.
- Cardiopulmonary exams: These exams assess heart and lung functioning to predict any potential cardiac or respiratory risks during and after surgery.
- Gastrointestinal evaluations: These include tests like upper endoscopy to check for H.pylori, ulcerations, or other potential stomach issues.
- Psychiatric Evaluation: It’s essential to assess mental health before surgery since managing postoperative changes and expectations demand psychological readiness.
Preoperative Diet
Adopting a preoperative diet is essential when preparing your body for lose weight surgery options. The primary objective of this diet is to decrease the liver size and minimize the amount of fat in the abdominal region. This diet commonly involves:
- High Protein Intake: Consuming a high-protein diet can help preserve muscle tissue while aiding fat loss.
- Low-Carbohydrate Foods: Lowering carbohydrates can help deplete glycogen stores in your body, prompting it to use stored fat for energy, contributing to fat loss.
- Reduced Calorie Intake: A reduced-calorie diet provides fewer calories than your body needs, forcing it to burn fat as a source of energy.
- Cutting Out Certain Foods and Drinks: Alcohol, caffeine, sugar-sweetened beverages, and high-fat foods are examples of what’s typically eliminated in the preoperative diet.
Patients often commence the preoperative diet two to three weeks before surgery, but the timeline can vary based on a physician’s recommendation.
Building a Support Network
In the journey towards lose weight surgery options, post-surgery lifestyle alterations could pose a substantial challenge. Thus, assembling a support network becomes a vital component of the preparation phase. This network could include:
- Medical Team: Engage with your bariatric surgeon, dietitian, and general practitioner who can provide necessary medical advice and support.
- Psychologist or Counselor: A mental health professional can offer strategies to cope with emotional stressors related to undergoing surgery and the changes that follow.
- Bariatric Support Groups: Connecting with others undergoing a similar process can provide a sense of community, shared understanding, and tips for navigating the journey.
- Friends & Family: Emotional support from loved ones is critical in managing the emotional transitions associated with weight loss surgery.
Lifestyle Changes and Postoperative Care for Lose Weight Surgery Options
Following bariatric surgery, postoperative care and lifestyle changes play an essential role in achieving successful weight loss and improving overall health. This involves several key areas, including:
Maintaining a Balanced, Nutrient-Dense Diet
Adapting new dietary habits is a critical aspect of life after weight loss surgery. This includes:
- Portion Control: Since surgery reduces the size of your stomach, eating smaller, more frequent meals can aid in digestion and prevent discomfort.
- High-Protein Foods: A protein-rich diet is crucial in preserving muscle mass during the weight loss process. Including lean meats, low-fat dairy, eggs, and plant-based protein sources can help meet protein requirements.
- Lower Intake of Sugars and Fats: Consuming foods high in sugar and fat can lead to complications, such as dumping syndrome, where food moves too quickly from the stomach to the small intestine.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is essential but avoid drinking fluids during meals to prevent overfilling your smaller stomach.
- Vitamin and Mineral Supplements: Due to reduced food intake and potential malabsorption, taking prescribed supplements can help secure essential nutrition.
Regular Physical Activity
Exercise has immense benefits following bariatric surgery, such as boosting weight loss, improving cardiovascular health, enhancing mood, and fostering general well-being. Some key points to consider:
- Gradual Introduction: Initially, patients should stick to gentle activities like short walks. As strength and endurance improve, incorporate aerobic exercises, muscle-strengthening activities, and flexibility exercises.
- Consistency is Vital: Aim for consistency rather than intensity. Gradually aim for about 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity physical activity per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities.
- Prevent Injury: Ensure to warm up before exercising and cool down afterwards to prevent injury. Listen to your body and avoid pushing too hard too soon.
Emotional Support & Counseling
When contemplating lose weight surgery options, navigating the surgery process and adapting to refreshed lifestyle habits can be emotionally taxing. Consequently, providing psychological support becomes a critical aspect of the process:
- Professional Counseling: Psychologists or counselors can help navigate emotional challenges, manage expectations, cope with changes in body image, and address potential eating disorders.
- Peer Support: Bariatric support groups, either in person or online, can provide a sense of community and a platform to share experiences, tips, and encouragement.
- Family and Friends: Lean on your loved ones for emotional support. They can also play a motivating role in maintaining your new dietary and exercise habits.
Remember, transitioning to a new lifestyle after weight loss surgery is a gradual process. It’s okay to encounter hurdles along the way: seek help, stay motivated, and keep your long-term health goals in sight. By incorporating these sustainable changes, you can improve the quality of your life and enjoy the results of your journey.
Risks and Complications of Bariatric Surgery
Though lose weight surgery options like bariatric surgery can yield substantial weight loss and health improvements, it’s crucial to recognize the possible risks and complications. Awareness of these factors can assist you in making informed decisions, adhering to postoperative guidelines, and timely addressing any arising issues.
Surgical Complications
Surgical complications can occur during or shortly after the surgery. Some common issues include:
- Infection: Surgical site infections can occur, especially in patients with obesity and diabetes. Doctors usually prescribe antibiotics to prevent infections and encourage proper wound care.
- Blood Clots: Blood clots can develop in the legs (deep vein thrombosis) and travel to the lungs (pulmonary embolism). To minimize this risk, patients are usually advised to move around as early as possible postoperatively and might receive blood-thinning medications.
- Gastric Leaks: A gastric leak may occur at the surgical connection points, requiring immediate medical attention. Symptoms include rapid heart rate, fever, or abdominal pain.
- Bleeding: Some bleeding can occur during surgery, and in rare cases, postoperative bleeding might require blood transfusion or additional surgery.
Nutritional Deficiencies and Side Effects
As bariatric surgery alters the digestive system, potential nutritional deficiencies and side effects may arise:
- Vitamin and Mineral Deficiency: Due to reduced food intake and malabsorption after particular procedures, vitamin and mineral deficiencies can emerge. Supplements, as recommended by your doctor, are vital to maintain sufficient nutrient levels.
- Dumping Syndrome: Consuming high-sugar and high-fat foods after gastric bypass may lead to rapid stomach emptying, or dumping syndrome, causing nausea, dizziness, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps.
- Gastric Stricture or Stenosis: A narrowing of the stomach or the passage connecting to the small intestine can occur, increasing the risk of vomiting and difficulty swallowing.
- Gallstones: Rapid weight loss might increase the risk of gallstone formation. In some cases, surgeons may remove the gallbladder during bariatric surgery to prevent this complication.
Long-Term Complications
Bariatric surgery can lead to certain long-term complications if patients do not adhere to postoperative guidelines:
- Weight Regain: Failing to maintain a balanced diet and consistent exercise routine may result in weight regain, undermining the surgery benefits.
- Excess Skin: Substantial weight loss may lead to excess skin, which can be both a cosmetic and psychological concern for patients. Some patients opt for body contouring surgery to address this issue.
- Mental Health Challenges: Adjusting to new lifestyle habits and body image changes can affect mental health. Seeking psychological support is crucial to manage these challenges.
Finally
Bariatric surgery can be a highly effective weight loss strategy for individuals struggling with severe obesity and related health conditions. It is important to consider the benefits, risks, and long-term commitment required for maintaining a healthy lifestyle after surgery to achieve lasting success.

What is the best surgery for weight loss?
The "best" weight loss surgery is different for each individual, as it depends on factors such as the patient's specific health conditions, weight loss goals, and personal preferences. Some common weight loss surgery options include Gastric Sleeve, Gastric Bypass, and Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch. Consulting with a bariatric surgeon will help determine the most suitable option.
What is the safest surgery for weight loss?
The safety of a weight loss surgery is subjective, as it depends on the clinical expertise of the surgeon, the patient's health, and other factors. In general, Gastric Sleeve and Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG) have lower complication rates compared to other bariatric surgeries, but it is essential to discuss potential risks with your healthcare team.
What are the 3 types of weight loss surgery?
Three common types of weight loss surgery are:
- Gastric Sleeve (Sleeve Gastrectomy) - Involving the removal of a significant portion of the stomach, leaving a smaller, banana-shaped sleeve.
- Gastric Bypass (Roux-en-Y) - Creating a small pouch from the stomach and rerouting the small intestine to connect to this pouch, limiting food intake and nutrient absorption.
- Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD-DS) - A more complex procedure that combines restriction and malabsorption by creating a smaller, tubular stomach and bypassing a large segment of the small intestine.
What are the 4 types of weight loss surgery?
Four common types of weight loss surgery include:
- Gastric Sleeve (Sleeve Gastrectomy)
- Gastric Bypass (Roux-en-Y)
- Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD-DS)
- Stomach Intestinal Pylorus Sparing Surgery (SIPS or Loop Duodenal Switch) - A modification of the traditional duodenal switch, removing a smaller portion of the stomach and bypassing a loop of the small intestine.
What is the most painless weight loss surgery?
Each weight loss surgery involves some level of discomfort or postoperative pain. Endoscopic procedures such as Intragastric Balloon and Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG) tend to be less invasive and have less postoperative pain compared to traditional surgical methods. However, pain varies among patients, and your healthcare team will prescribe appropriate pain-relief medications.
What can you never eat again after gastric bypass?
While gastric bypass patients can eventually reintroduce most foods into their diet, certain foods should be avoided or limited. These include:
- Sugar-filled foods and drinks (soda, candy, etc.) to prevent "dumping syndrome"
- High-fat and high-calorie foods (fried foods, full-fat dairy products)
- Tough meats and fibrous vegetables
- Carbonated beverages
- Caffeine
- Alcohol
It is vital to follow your healthcare team's dietary recommendations and focus on consuming protein-rich, nutrient-dense foods.